In today’s world, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is utilized for various purposes and tasks, making significant contributions to almost every industry. AI has become a vital aid in advancing innovation and building strategies for a sustainable future.
As researchers explore new methods and applications for AI, there is a potential for it to revolutionize human society entirely. However, will this type of intelligence eventually replace us?
Stepping Out of Science Fiction
AI has come a long way since its inception. Humanity stands on the brink of transformative change, leading world leaders to engage in debates about the question: “Will artificial intelligence dominate the world and control us?”
While such a scenario may not occur immediately, many hypotheses suggest potential negative impacts of AI in the future. It’s conceivable that future generations might be dominated by AI, influencing elements such as friendships, leadership skills, forgiveness, and eventually love.
Science fiction movies often reflect the fear surrounding AI. In “Star Wars,” for example, the conflict between C3PO and R2D2, who collaborate with the Rebel Alliance to stop the Empire, mirrors the struggles between HAL 9000 and Ex-Machina – both trying to assassinate their human creators.
These fictional scenarios primarily depict the physical impact of AI on humans, with little emphasis on its potential effects on social relationships. In other words, in the future society, the interactions between humans might be shaped by artificial intelligence.
The Human-AI Interaction in the Past
Back in the 1940s, the interaction between humans and AI was still a distant prospect. Isaac Asimov, the renowned science fiction writer, introduced three laws for robots. The purpose of these laws was to ensure that AI or robots would not cause harm to humans. Through these laws, Asimov suggested that robots would genuinely impact humans through direct interactions.
Today, AI surrounds us everywhere. We have voice-activated search devices on our phones, smart devices in our homes like Google Home, Echo Dot, and countless AI-driven applications on smartphones. We have household robots, surgical robots, and even human-like robots.

As humanity strives to outmatch its own technological achievements, we are also continuously refining artificial intelligence. Consequently, machines might become the targets of emotions and affections.
The science-fiction movie “Her” revolves around an introverted writer who forms a romantic bond with an AI-powered operating system. The protagonist is enticed by the AI’s ability to learn and adapt. While this might not happen immediately, research indicates that humans may develop romantic relationships with AI in the future.
“Citizenship Rights of the Robot World”
Dr. Maciej Musial from Adam Mickiewicz University in Poznan, Poland, points out that humans will soon become dependent on robots and AI applications. The evidence for this phenomenon can already be seen in reality: Humans are becoming increasingly attached to AI, particularly smartphones.
Furthermore, we are forming emotional connections with AI in various ways. Humans tend to anthropomorphize objects. Studies on how we emotionally bond with household devices like robot vacuum cleaners reveal that many owners will clean the house themselves if they sense their robots are “feeling down.” Car and bicycle owners often give names to their vehicles.
It is conceivable that the day when humans develop serious emotional relationships with robots is not far away. And who knows, one day these human-robot relationships may become a societal norm, leading to marriages between humans and robots.
David Hanson, the creator of the famous robot Sophia, suggests that within a few decades, humans might marry robots. In fact, there are already robots designed to comfort lonely individuals in today’s modern society.
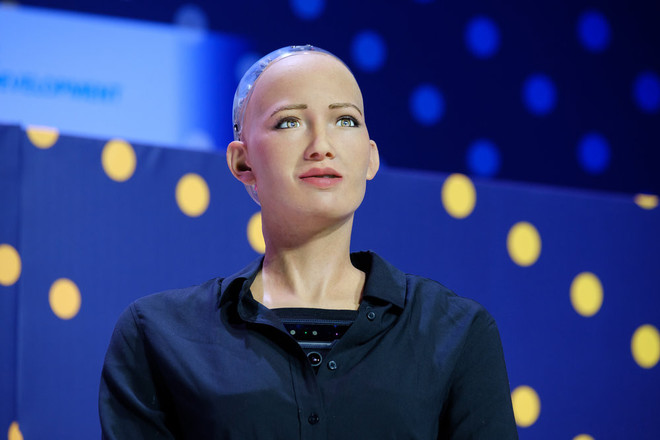

Hanson also speculates that robots will possess rights similar to humans by 2045, including land ownership, voting rights in general elections, and even legal marriage.
In conclusion, he proposes a hypothetical scenario in 2035, where robots might perform most human tasks. They may even gain “Citizenship Rights of the Robot World” by 2038, compelling leaders to establish equality for them in the human world.
Related articles: https://newyorknews9.com/microsoft-puts-a-steep-price-on-its-latest-ai-powered-tool/
By NewYork News9 and GPT










